
Case Study:
Inclusive Design in Online Learning

Mohawk's accessibility researchers, along with students in the Accessible Media Production Program, provide expertise to help industry solve their digital accessibility challenges, combining accessibility and usability knowledge to deliver solutions that help organizations meet their accessibility (AODA/WCAG) requirements. Each project is approached with an accessible and evidence-based research lens looking at an industry problem, proposing a solution, and then working on applying their knowledge to address the solution.

Project Summary
Project Team: Allison Fitzgibbon (student researcher), Jennifer Jahnke (faculty advisor)
The Inclusive Design in Online Learning project explored barriers to inclusive online learning for college students during the conversion to remote learning.
By identifying student and faculty needs, the project results have encouraged faculty to implement inclusive teaching practices in the online environment by providing them with key tools to redesign their course materials using simple intuitive design and inclusive practices.
The Inclusive Design in Online Learning project provided faculty with a course template for the design and delivery of accessible educational materials while adhering to principles established through Universal Design for Learning (UDL), Differentiated Instruction, and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines for the sharing of digital educational materials. Hundreds of college faculty and staff in over 15 post-secondary institutions, across Canada and internationally have benefitted from this project. The template is also available in D2L’s online Accessibility Lab.
Teaching and Learning Challenge
There are many factors that are driving the need for inclusive teaching practices. Over 22% of Canadians aged 15 and older have disabilities that may interfere with their ability to access and share information; post-secondary institutions have a responsibility to “create, provide, and receive information and communication that people with disabilities can access” (AODA.ca, 2019).
Additionally, with an increased demand for flexible learning options, it is important that post-secondary faculty are prepared to create accessible and inclusive courses that can be delivered remotely.
Finally, there are laws within Ontario and best practices globally that help ensure all individuals have equal access to information both in print and digital content.
Faculty Training Module
The Faculty Training Module is envisioned as a comprehensive way to provide faculty with relevant information about Universal Design for Learning (UDL), Differentiated Instruction, and Web Content Accessibility Guidelines.
The module reviews the importance of respecting student voice and choice by highlighting a student's readiness to learn and learning preferences while paying specific attention to individual versus group work in the online environment. Faculty learn multiple ways of presenting information digitally, such as recorded lessons with closed captions, accessible PowerPoints, and lesson transcripts. The module also explores techniques for engaging students in an online or remote class, using interactive activities, online collaboration tools or H5P (an open-source content collaboration framework based on Javascript).
What Faculty Learn

LMS Compatability
Most post-secondary faculty are required to post learning materials in a shared Learning Management System (LMS). It is important that these materials and how they are accessed are designed to meet accessibility standards from the very beginning. With the increase in remote learning, it is especially important that faculty work to ensure that courses are as accessible as possible for all potential learners.

Legislation
Education is a fundamental human right and individuals with disabilities have a right to equal access to post-secondary education. In Ontario, additional legislation targets individuals’ rights to accessible information and communication, including the right to accessible books and learning resources. Faculty discover why it is urgent and necessary to create accessible course materials.

Web Content
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide standards for producing online content, with a focus on the content being Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust. Faculty learn how to create accessible lessons while adhering to Web Content Accessibility Guidelines to ensure the information they share can be accessed and understood by all learners, including those who use assistive technologies.

Students First
A literature review and applied research revealed that students need consistency in the course layout for ease of navigation and predictability of content; they need clarity about expectations; they need to trust that embedded links and activities will work; and they need accessible educational materials, including videos with closed captions, transcripts, and downloadable conversion-ready files.

Barriers to Adoption
Faculty barriers to designing accessible or barrier-free content include misconceptions about disabilities, a lack of time and training in creating content, and a lack of immediate, usable resources. This led to the development of a downloadable course template for faculty use. It addresses the barriers by guiding the structure and navigation of their online courses while adhering to accessibility standards and guidelines.
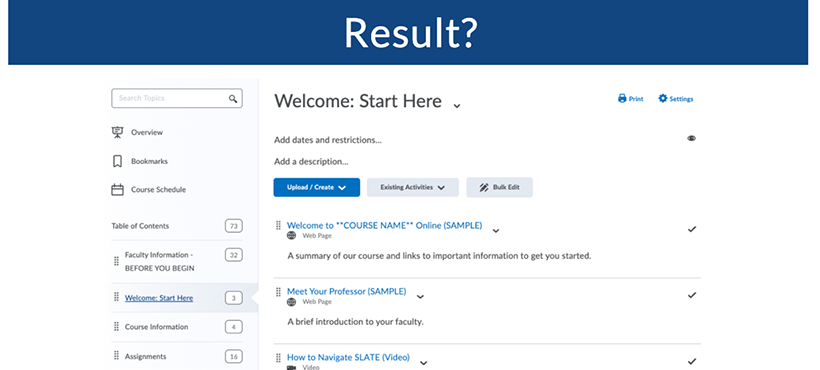
Course Template
The Inclusive Design for Online Learning course template includes page templates designed to pass the coulour contrast analyzer for web content, modules of online lessons and supporting documents, and prompts to consider UDL in the design and facilitation of lessons and assessments. Faculty are also taught how to create and embed accessible materials for a diverse community of learners.

